Security scanning is critical for maintaining infrastructure health, but manually checking scan results introduces delays and potential oversight. This guide demonstrates how to automate Nessus scan notifications using n8n workflows and Discord webhooks, ensuring your team gets immediate visibility into security findings.
Prerequisites
- Nessus scanner with API access enabled
- n8n instance (self-hosted or cloud)
- Discord server with webhook permissions
- Basic understanding of API authentication
Architecture Overview
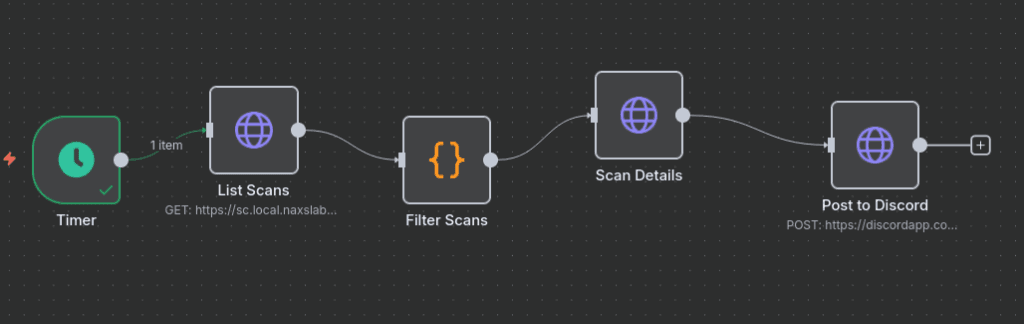
The automation workflow consists of:
- Schedule Trigger: Polls Nessus API at regular intervals
- Scan Detection: Identifies completed scans
- Data Retrieval: Fetches detailed scan results
- Message Formatting: Structures data for Discord
- Notification Delivery: Sends formatted alerts to Discord
Setting Up Nessus API Access
First, generate API credentials in your Nessus instance:
- Navigate to Nessus web interface
- Go to Settings → My Account → API Keys
- Generate new API key pair (access key + secret key)
- Store these securely for workflow configuration
The Nessus API uses a custom authentication header format:
X-ApiKeys: accessKey=YOUR_ACCESS_KEY; secretKey=YOUR_SECRET_KEY
Important authentication notes:
- Case sensitivity matters:
accessKeynotaccesskey - Use semicolon separation, not JSON format
- Both
Content-Type: application/jsonandAccept: application/jsonheaders are required
Configuring Discord Webhook
Create a webhook in your target Discord channel:
- Open Discord channel settings
- Navigate to Integrations → Webhooks
- Create new webhook
- Copy the webhook URL (contains authentication token)
Discord webhooks require no additional authentication – the URL itself provides channel access.
Building the n8n Workflow
Development Approach
Start with Manual Trigger for development and testing:
- Build and debug each step manually
- Test API connections and data flow
- Verify Discord message formatting
Convert to automated scheduling once tested:
- Replace Manual Trigger with Schedule Trigger
- Set appropriate polling interval (5-10 minutes)
1. Initial Scan List Retrieval
Configure HTTP Request node for scan enumeration:
Node Configuration:
- Method: GET
- URL:
https://your-nessus-server:8834/scans - Authentication: None (use headers)
- Headers:
X-ApiKeys: accessKey=YOUR_ACCESS_KEY; secretKey=YOUR_SECRET_KEYContent-Type: application/jsonAccept: application/json
SSL Configuration: If using self-signed certificates or encountering SSL validation errors with Let’s Encrypt, enable “Ignore SSL Issues”. This maintains encryption while bypassing Node.js strict certificate chain validation.
2. Scan Filtering and Duplicate Prevention
Add Code node to process scan responses with time-based filtering:
const response = $input.all()[0].json;
// Extract scan data from API response
console.log('Nessus API Response:', JSON.stringify(response, null, 2));
// Validate response structure - exit if no scans exist
if (!response.scans || response.scans.length === 0) {
console.log('No scans found - ending workflow');
return [];
}
console.log(`Found ${response.scans.length} scan(s)`);
// Log all scans for debugging visibility
response.scans.forEach(scan => {
console.log(`Scan: ${scan.name} (ID: ${scan.id}) - Status: ${scan.status}`);
});
// Filter for completed scans only - ignore running/failed scans
const completedScans = response.scans.filter(scan => {
return scan.status === 'completed';
});
console.log(`Found ${completedScans.length} completed scans`);
if (completedScans.length === 0) {
console.log('No completed scans yet - waiting for scans to finish');
return [];
}
// Time-based duplicate prevention - only notify about recent scans
// Prevents re-notification of old scans on every workflow execution
const oneDayAgo = Date.now() / 1000 - (24 * 60 * 60);
const recentScans = completedScans.filter(scan => {
return scan.last_modification_date > oneDayAgo;
});
console.log(`Found ${recentScans.length} scans completed in last 24 hours`);
if (recentScans.length === 0) {
console.log('No recent completed scans to notify about');
return [];
}
// Return recent scans for detailed processing
// Each scan becomes a separate workflow item
return recentScans.map(scan => ({ json: scan }));
Key Implementation Details:
- Time-based filtering: Simpler than state management, prevents notification spam
- Console logging: Essential for debugging workflow execution
- Status filtering: Only process scans with “completed” status
- Array mapping: Each scan becomes a separate workflow item for parallel processing
3. Detailed Scan Results Retrieval
Configure second HTTP Request for comprehensive scan data:
Node Configuration:
- Method: GET
- URL:
https://your-nessus-server:8834/scans/{{Number($json.id)}} - Same authentication headers as scan list retrieval
Critical Note: Use {{Number($json.id)}} conversion. Nessus API expects integer scan IDs, not strings. Using {{$json.id}} directly will result in “Invalid ‘scan_id’ field: invalid type ‘string’, expecting ‘int'” errors.
4. Discord Message Formatting
Configure Discord webhook node with dynamic JSON:
Node Configuration:
- Method: POST
- URL: Your Discord webhook URL
- Headers:
Content-Type: application/json - Body Content Type: JSON
- Specify Body: Using JSON
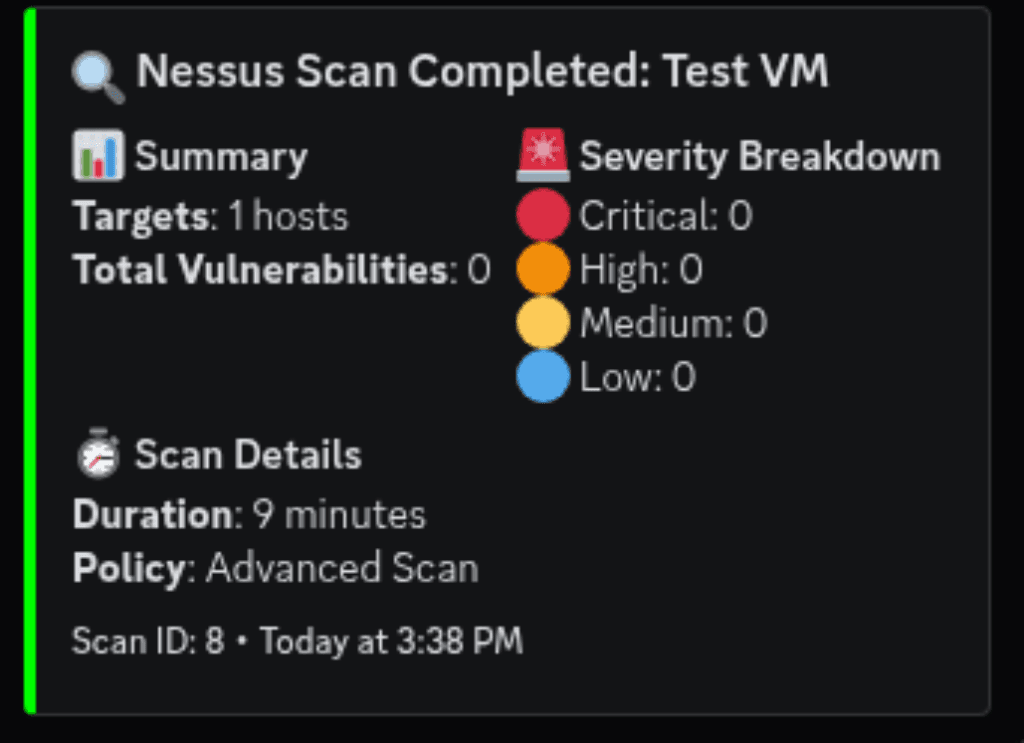
JSON Message Template:
{
"embeds": [{
"title": "🔍 Nessus Scan Completed: {{$json.info.name}}",
"color": 65280,
"fields": [
{
"name": "📊 Summary",
"value": "**Targets**: {{$json.hosts.length}} hosts\n**Total Vulnerabilities**: {{$json.hosts.reduce((sum, host) => sum + (host.critical || 0) + (host.high || 0) + (host.medium || 0) + (host.low || 0), 0)}}",
"inline": true
},
{
"name": "🚨 Severity Breakdown",
"value": "🔴 Critical: {{$json.hosts.reduce((sum, host) => sum + (host.critical || 0), 0)}}\n🟠 High: {{$json.hosts.reduce((sum, host) => sum + (host.high || 0), 0)}}\n🟡 Medium: {{$json.hosts.reduce((sum, host) => sum + (host.medium || 0), 0)}}\n🔵 Low: {{$json.hosts.reduce((sum, host) => sum + (host.low || 0), 0)}}",
"inline": true
},
{
"name": "⏱️ Scan Details",
"value": "**Duration**: {{Math.round(($json.info.scan_end - $json.info.scan_start) / 60)}} minutes\n**Policy**: {{$json.info.policy}}",
"inline": false
}
],
"timestamp": "{{new Date().toISOString()}}",
"footer": {
"text": "Scan ID: {{$json.info.object_id}}"
}
}]
}
Expression Details:
{{$json.info.name}}: Dynamic scan name{{$json.hosts.length}}: Actual scanned host count (more accurate than configured targets){{$json.hosts.reduce(...)}}: Real-time vulnerability calculations{{Math.round(...)}}: Duration calculation in minutes{{$json.info.object_id}}: Actual scan ID for reference
Troubleshooting Common Issues
SSL Certificate Validation Errors
Error: UNABLE_TO_VERIFY_LEAF_SIGNATURE or similar certificate chain errors
Cause: Node.js has stricter certificate validation than browsers, especially with Let’s Encrypt intermediate certificate chains.
Solution: Enable “Ignore SSL Issues” in HTTP Request node options. This maintains full encryption while bypassing validation strictness.
API Authentication Failures
Error: {"error":"Invalid Credentials"}
Verification Steps:
- Check header case sensitivity (
accessKeynotaccesskey) - Verify semicolon separation in authentication header
- Ensure no extra spaces or formatting issues
- Test credentials with curl for validation
Data Type Conversion Errors
Error: Invalid 'scan_id' field: invalid type 'string', expecting 'int'
Solution: Always use {{Number($json.id)}} for scan ID references in URLs. Nessus API requires proper data type conversion.
Duplicates
This method produces duplicates that I haven’t fixed at the time of this writing. This is because the workflow has no memory of which specific scan IDs have already been processed – every time it runs, it treats all completed scans as “new” and sends notifications for them again.
Conclusion
Automated security scan notifications significantly reduce incident response times while ensuring consistent monitoring coverage. The n8n workflow approach demonstrated here provides flexibility for customization while maintaining operational simplicity.





